Theme: New Technologies in Treatment : Liver and Stomach Defects
Gastroenterology 2022
On Behalf of the Organizing Committee, We welcome you to this signature event of the year 28th World Conference on Gastroenterology & Hepatology, which is on June 13-14, 2022 in Amsterdam, Netherlands, where you’ll make sure to possess a meaningful experience expertly from around the globe. The Conference program will be both exciting and ground-breaking in its wide ranging and multidisciplinary content. In addition to traditional abstract presentations and keynote lectures by world renowned invited speakers, we will be offering workshops and interactive sessions as well as several exhibitors.
We are happy to inform you that we are organizing the conference with the theme of New Technologies in Treatment: Liver and Stomach Defects. We take great pleasure in welcoming academic scientists, research scholars, researchers, students and experts of Gastro & Hepatology.
DETAILS OF THE CONFERENCE
|
CONFERENCE NAME |
THEME |
DATE |
LOCATION |
|
Gastroenterology Congress 2022 |
New Technologies in treatment: Liver and Stomach Defects |
June 13-14, 2022 |
Amsterdam, Netherlands |
FEATURES OF CONFERENCE:
- To investigate the Innovative methodologies of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
- Perfect platform for global networking.
- Ongoing examination work, new procedures in the Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
- Collaborative Research opportunities.
- The current update in the field of Gastroenterology, Hepatology
- Freedoms for participants to share their work.
- Make a sprinkle with another item offering.
- Structured workshops, events and symposia.
- Panel discussions & interactive sessions.
- Participate in world session including live Q&A.
Target Audience:
- Hepatology Professors
- Gastroenterology Professors
- Internal Medicine Physicians
- Healthcare Institutions
- Researchers and Scholars
- Pharmaceutical organizations
- Members of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Associations
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology Students
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology Scientists
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology Researchers
- Companies producing clinical gadgets
Why to Attend:
- Our extensive online promotion attracts over 20,000 users and 60000 views to our Library of Abstracts, giving the researchers and presenters who participate in our conferences worldwide exposure.
- Workshops on Career Guidance for Graduates, Doctorates, and Postdoctoral Researchers
- Fellows in Post-Doctoral Research
- Accepted abstracts will appear in PubMed, MEDLINE, and other databases.
- SCOPUS, SOCOLAR, EBSCO, CAS, Index Copernicus, and Google are just a few of the databases available.
- Journals indexed by Scholar, SCIRUS, and DOAJ.
- Each abstract will be given a Digital Object Identification number means DOI.
- Cross Ref provided a Digital Object Identifier means DOI.
- Google's Speaker and Abstract pages for your name would be useful.
- Your scientific profile will be grant all around the world.
- The conference brings together scientists and business leaders.
Session no.1: Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology is the study of normal functioning and disorders of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, pancreas, gallbladder, bile ducts, and liver. This includes common and important diseases such as colon polyps and cancer, hepatitis, gastro esophageal reflux disease (heartburn), digestive ulcers, colitis, gallbladder, bile duct disease, malnutrition, irritable bowel syndrome, and pancreatitis. It includes a point-by-point examination of the gastrointestinal organs' normal action (physiology), which includes material movement through the stomach and digestive system, absorption and retention of supplements in the body, waste removal from the body, and the liver's capacity as a digestive organ.
- IBS and Chronic Constipation
- Gallbladder and Biliary Disease
- Pancreatitis
- Microbiome
Session no.2: Gastrointestinal Infection and Viral Gastroenteritis
Viral gastroenteritis is an intestinal infection that includes signs and symptoms such as watery diarrhea, gastric spasm, nausea and vomiting, and sometimes fever.The most common way to develop viral gastroenteritis (often called gastroenteritis) is to contact an infected person or eat contaminated food or water. If you are otherwise healthy, you may recover without complications. However, viral gastroenteritis can be fatal to infants, the elderly, and people with weakened immunity.
- Rotavirus
- Adenovirus
- Bacterial gastroenteritis
- Bacillary dysentery
Session no. 3: Gastrointestinal Pharmacology
Gastrointestinal disorders necessitate therapy, and pharmacological therapies are divided into two categories: physician-recommended pharmaceuticals and over-the-counter medications (OTC Drugs). The drugs are administered to address issues with the gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract dividers, and gastrointestinal motility. The study of the characteristics and activities of medications that influence the gastrointestinal tract is known as gastrointestinal pharmacology. It is in charge of:
- providing essential nutrients to the body
- Maintaining optimal blood levels of all vital nutrients to allow for normal activities
- Toxic waste inside the body is avoided by eliminating wastes obtained from the diet and some products of the body's metabolism
Session no. 4: Gall Bladder Cancer Treatment
The treatments are used to treat localized and locally progressed gallbladder cancer:-The gallbladder and portions of the surrounding tissue are removed during surgery. A portion of the liver, as well as adjacent lymph nodes may indeed be removed. Surgery, you may get radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy. Radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy is a treatment option. Radiation treatment using radio sensitizers in a clinical study
- Surgery to remove the gallbladder
- Radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy
- A clinical trial of radiation therapy with Radiosensitizers
Session no. 5: Advance Nutrition and Dietetics in Gastroenterology
Advanced Nutrition and Dietetics in Gastroenterology covers the relationship between nutrition and food and the gastrointestinal tract in a comprehensive and up-to-date manner. It investigates the role of dietary variables in the development of a range of gastrointestinal illnesses, as well as the effects on diet and treatment options. The term probiotics is now used to refer to ingesting microorganisms that are relevant to the interests of humans and animals. Probiotics have many benefits, including reducing gastrointestinal stress, improving immune health, and relieving constipation. Dietary enzymes and unicellular proteins can be used as dietary supplements. Gastrointestinal GI is mainly responsible for the following:
- Acquiring and digesting food
- Absorbing nutrients and water
Session no. 6: Gastrointestinal Oncology
Tumors of the Gastrointestinal tract and other organs showing signs of internal death, severe distress, distension, dysphagia or persistent constipation or inability to handle severe bowel movements. Gastrointestinal oncology is a broad term that refers to the treatment of various malignancies of the gastrointestinal tract and gastrointestinal tract also called stomach cancer. This indicates that the malignant state of gastrointestinal cancer is the most common form of cancer. Treatment of GI cancer depends on the type of cancer, the stage of the cancer, and how the cancer spreads. Diseases that can be treated with gastrointestinal oncology include:
- Esophageal Cancer
- Anal Cancer
- Stomach (Gastric) Cancer
Session no. 7: Gastrointestinal Disorders
Thousands of years have gone since the first use of such records in medicine. Modern medical guidelines are based on a review of current facts under the paradigm of evidence-based medicine, as opposed to prior approaches, which were typically based on tradition or authority. They frequently consist of succinct consensus statements on healthcare guiding principles. Clinical practice guidelines and other articles on gastrointestinal problems are available. Human gastrointestinal illness is caused by a variety of disease-causing microbes or germs that can be acquired by consuming contaminated food or beverages, coming into contact with contaminated recreational water, coming into contact with infected animals or their environments, or coming into contact with infected persons.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Hemorrhoids
- External hemorrhoids
- Internal hemorrhoids
Session no.8: Kidney and Pancreas Transplant
A kidney-pancreas transplant is a procedure that involves putting both a kidney and a pancreas into someone who suffers kidney failure caused by type 1 diabetes. Both transplanted organs may come from the same deceased donor in many circumstances. The success rates for combined kidney-pancreas transplants from dead donors are also very high. When both the pancreas and a kidney originate from the same donor: a deceased donor, the best results are frequently obtained. This is due to the fact that the chances of being rejected are substantially lowered. However, several living donor transplants have been completed, with one kidney and a pancreatic segment being donated.
- Blood clots and bleeding
- Leaking from or blockage of the tube
- Infection
- Failure or rejection of the donated kidney
Session no.9: Liver & Intestine Transplant
Patients who have had an intestine transplant have a one-year survival rate of more than 85%, which is equivalent to patients who have had a liver transplant. The number of organs suitable for transplantation will considerably rise if damage is reduced. The new technology perfusion machine maintains the liver in a physiological state and keeping it warm and pumping it with blood, nutrients. This can help the liver heal from any damage it may have received during the donor's removal.
- Graft loss
- Erebral Edema, or intracranial hemorrhage
- Graft survival rates
- Small bowel transplantation
Session no. 10: Gastrointestinal Diseases during Pregnancy
There are many gastrointestinal problems are frequent, even if you may not had any before getting pregnant. Because they differ, the reasons can also differ. some of the most common causes or risk factors for gastrointestinal problems during pregnancy are Changes in hormones, GI motility disorders, Obesity, Certain medications, Poor diet, stress and other. Chronic gastrointestinal disorders demand treatment continuation during pregnancy, posing the intriguing question of whether the mother's benefits may be hazardous to the unborn child. Furthermore, some infections, such as acute fatty liver of pregnancy, develop only during pregnancy, necessitating emergency interventions such as preterm delivery.
- High blood pressure
- Gestational diabetes
- Preeclampsia
- Preterm labor
Session no. 11: Neuro gastroenterology Disorder
Neuro-gastroenterology is the study of the brain. Disorders of Neuro gastroenterology and motility (NGM) are frequent and have a substantial health-care cost. Despite the fact that pediatric gastroenterology fellows are supposed to get extensive training in the diagnosis and management of NGM illnesses, there is still a concern about unfulfilled training demands and a lack of experience treating patients with NGM disorders. He goal of our research was to learn more about pediatric gastroenterology fellows' NGM training experiences in North America and to see how that experience influenced their interest in a career in neuro gastroenterology GM issues.
- Pernicious anemia
- Nicotinamide deficiencies
- Thiamine deficiencies
- Coeliac disease
Session no. 12: Advanced Research in Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Advanced Research in Gastroenterology and Hepatology is a peer-reviewed, open-access international medical journal that publishes biweekly and covers all aspects of gastroenterology and hepatology. Gastroenterology is a medical specialty that deals with the digestive system and its problems. Advanced Research in Gastroenterology and Hepatology, or hepatobiliary medicine, is a sub-specialty of gastroenterology that studies the liver, pancreas, and biliary tree, whereas proctology is a sub-specialty of general surgery that studies the anus, rectum, and colon.
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Intussusception
- Liver Abscess
- Pancreatic Exocrine Cancer
Session no. 13: Disease of Liver Cancer
The cause of liver cancer is well known, for example, in chronic hepatitis infections. However, liver cancer can occur in people without underlying disease, and the cause is not clear Liver disease can be acquired (hereditary) or caused by many factors that damage the liver, such as infections and alcohol consumption. Obesity is also associated with liver damage. Over time, damage to the liver can cause scarring (cirrhosis), which can lead to life-threatening liver failure.
- Cirrhosis
- Exposure to aflatoxins
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Session no. 14: Advanced Hepatology
As the field of general hepatology continues to evolve and expand, and the number of cases of liver transplantation increases, the need for hepatologists who are qualified to treat patients with chronic liver disease and liver transplantation has dramatically increased. Hepatology is a branch of medicine related to the study, prediction, analysis, and treatment of infectious diseases that affect the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas. The future of hepatology has promised to eradicate hepatitis C virus infection, and new challenges have begun. Therefore, in-depth training is very necessary to acquire additional knowledge and skills in this particular subfield of gastroenterology. In November 2006, the American Board of Internal Medicine began offering certification exams for transplanted hepatology. It is now recognized as a discipline in its own right.
- Trans hepatic pancreato-cholangiography
- Trans jugular intrahepatic Porto systemic shunt
Session no. 15: Hepatitis Infections
Hepatitis refers to an inflammatory disease of the liver. Often the result of a viral infection, hepatitis has other possible causes. These include autoimmune hepatitis and hepatitis that occurs as a secondary result of drugs, drugs, toxins, and alcohol. Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Alcohol intake, various health conditions, and some medications can cause this condition. However, viral infections are the most common cause of hepatitis. The five major viral classifications of hepatitis are
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis D
- Hepatitis E
Session no. 16: Hepatitis Vaccination
For total protection, you should have two doses of the hepatitis A vaccination, given as shots six months apart. The virus contained in the vaccine is destroyed (inactive). Depending on the type of vaccination administered, three to four doses are required for long-term immunity. You get them in the form of shots. The first dose should be given at birth, and the series should be completed by the age of six months. A second dosage is usually given at one month and a third dose at six months.
- Engerix B VACCINE
- Heplisav-B VACCINE
- Recombivax HB
Session no. 17: Hepato-pancreato-biliary disease
Darker urine color, and lighter stool color are all common symptoms or side effects of these illnesses. Any abnormality of the hepatobiliary system that hinders its normal function is referred to as hepatobiliary disease. It can range from a small infection or scarring to more serious illnesses like cancer. The liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts are the organs of the hepatobiliary system. Some are caused by congenital or inherited factors; the majority is caused by persistent injury to the tissues of the affected organs.
- Gallstones
- Biliary obstruction
- Biliary epithelium
- Liver parenchyma
Session no. 18: Peptic Ulcer Disease
Ulcers can form in any part of the GI tract that comes into contact with gastric secretion, including the lower esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Ulcers only form in the presence of an acidic environment. It is not required to have a lot of stomach acid to get an ulcer. When compared to a person with a duodenal ulcer, a person with a gastric ulcer has normal to less than normal gastric acidity. People used to believe that ulcers were caused by stress or certain meals. However, no proof has been produced to back up those views. Ulcers are caused by two main factors, according to research
- Bacteria Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
Session no. 19: Gastrointestinal and Minimally Invasive Surgery
The goal of an orthopedic surgical intervention is to treat a bone or anatomically associated structures such as cartilage, ligaments, or tendon. These tissues are typically found deep within the human body, necessitating significant surgical exposure to obtain access to the intervention's goals. There are three key reasons for the demand for less invasiveness:
- Implants, such as screws, nails, or endoprotheses, are used in numerous orthopedic developments.
- The surgeon must be able to see the operation field.
- Surgical devices must have an effect on the bone.
Session no. 20: Metabolic liver diseases
The majority are caused by a metabolic pathway being disrupted by a deficiency in an enzyme or transport protein. This set of illnesses is distinct from what is referred to as metabolic disease. Adult metabolic syndrome, or more precisely metabolic syndrome, is a condition that affects adults. Visceral obesity is one among them. These illnesses are split into two categories.
- Another is alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency (A1ATD).
- Cystic fibrosis is a disease that affects the lungs (CF)
Session no. 21: Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is not a disease, it’s a functional disorder. In other words we can say that the Bowel doesn’t work as it should. In 2019, the global irritable bowel syndrome treatment market was worth USD 1.5 billion; with a CAGR of 10.1 percent expected during the forecast year. One of the most frequent illnesses affecting the large intestine is irritable bowel syndrome. Cramps, abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, gas, and constipation are all symptoms of this condition. Diet, lifestyle, and stress management can help some people manage their symptoms. Medication can be used to address more severe symptoms, and counseling does not induce intestinal tissue changes or raise your risk of colon cancer.
- IBS with diarrhea (IBS-D)
- IBS with constipation (IBS-C)
- mixed IBS (IBS-M)
Session no. 22: Obesity and Bariatric Surgery
Obesity is caused by an imbalance of calorie intake and utilization, as well as a lack of physical activity or a regular routine. The goal of this surgery is to reduce stomach capacity, limiting how much food the stomach can store at any given time and so encouraging early satiety. Its helps to prevent food from being digested, resulting in a reduction in the number of calories released into the body. Bariatric surgery, also known as metabolic surgery, is a weight-loss procedure done on people who are obese and want to lose weight.
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
- Adjustable gastric banding
- Sleeve gastrostomy.
Session no. 23: Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
Crohn's disease can occur anywhere between the mouth and the anus, but ulcerative colitis is restricted to the colon. There are healthy sections of the gut intermingled in between inflamed patches in Crohn's disease. On the other hand, ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammation of the colon. They both are the type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Seminerio, an assistant professor and director of the University of South Florida's Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, stated. "It's vital to categories whatever ulcerative colitis disease state you're dealing with utilizing severity index scores and endoscopic scores when you're talking about ulcerative colitis, especially, and you're in the mild to severe disease states”.
- Ulcerative colitis
- Microscopic colitis
- Pseudomembranous colitis
- Ischemic colitis
- Allergic colitis.
Session no. 24: Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Pathology
As we know GI (Gastrointestinal) bleeding is a sign of an illness, not a sickness itself. Hemorrhoids, peptic ulcers, rips or inflammation in the esophagus, diverticulosis and diverticulitis, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, colonic polyps, or cancer in the colon, stomach, or esophagus are all possible causes of GI (Gastrointestinal) bleeding. Gastroenterology bleeding continues to provide difficult investigative and management challenges. Excluding systemic illnesses, questioning about drug use, a search for parasites, barium studies, and a comprehensive endoscopic examination are all part of a standard study. If the tests come back negative, the patient most likely has one or more minor vascular anomalies in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Upper GI bleeding
- lower GI bleeding
- Internal hemorrhoids
- External hemorrhoids
- Anal fissures
Session no. 25: Hepatic Hemangioma
Hepatic Hemangioma (HH) Tumors in or on the liver are the most prevalent benign (noncancerous) tumors. The tumor is made up of a network of blood arteries, endothelial cells that line the blood vessels, and the hepatic artery, which serves as the mass's principal fuel supply. This tumor is also known as a cavernous or capillary hepatic hemangioma. The following are some of the indications and symptoms of a liver hemangioma:
- Typical hepatic haemangioma.
- Multifocal
- Diffuse
- atypical hepatic hemangioma
The Competitive Scenario is a perspective study of the suppliers' varied business growth strategies. This section's news provides vital insights at various stages while keeping up with the business and engaging players in the economic debate. Merger & Acquisition, Agreement, Collaboration, & Partnership, New Product Launch & Enhancement, Investment & Funding, and Award, Recognition, & Expansion are the categories that the competitive scenario represents. All of the information gathered assists the vendor in identifying market gaps as well as rival strengths and weaknesses, allowing them to improve their product and service.
The main challenge is that there is a shortage of trained physicians and endoscopists in the market. Endoscopic procedures must be performed by trained specialists to minimize the spread of infections in endoscopy facilities. The global lack of competent endoscopy physicians and nurses is predicted to have a detrimental influence on the number of endoscopic procedures performed each year. To address this issue, a few market players, such as Olympus, have developed training facilities. The organization has 22 endoscopic training centers in Asia alone. Such activities will raise awareness of the most recent technical breakthroughs in endoscopy while also increasing the number of qualified endoscopy experts. If we talk about the opportunities in the market of gastroenterology, In emerging economies, the healthcare sector is booming. , Russia Brazil, China, India and South Africa (BRICS) are among the fastest-growing economies in the world.
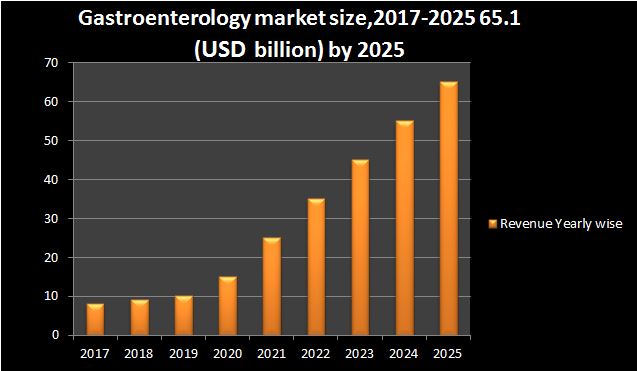
The global gastrointestinal therapeutics market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 6.5 percent between 2015 and 2020, reaching USD 13.8 billion. This increase in market size can be attributed to a number of factors, including rising biologics consumption, tentative approval of late-stage molecules, development of novel therapies using innovative technologies, and improved diagnostic tools, which has resulted in an increase in the number of people seeking treatment. Three regions were studied: the Americas, Asia-Pacific, and Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. In the Americas, Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, and the United States are all researched deeper
The market was investigated in three regions: the Americas, Asia-Pacific, and Europe, Middle East, and Africa. Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, and the United States are all studied further in the Americas.
Related Societies
· American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases
· American College of Gastroenterology
· American Gastroenterological Association
· American Motility Society
· American Physiological Society: Gastrointestinal Section
· European Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
· Gastroenterology Research Group
· International Group for the Study of Gastrointestinal Motility
· Scandinavian Association for Gastrointestinal Motility
· World Organisation of Gastroenterology (OMGE)
· Society of Mucosal Immunology (SMI)
Related Medical Companies
· Pfizer
· AstraZeneca
· Takeda Pharmaceuticals
· Vivante Health
· Clinipace Worldwide
· Seed Health
· Iterative Scopes
· Coral Genomics, Inc.
· Ferring Pharmaceuticals
· Allergan
· Odin Vision
· Edesa Biotech
· Suono Bio
· Novan Inc
· Bausch Health
· Sosei Group
· Progenity
· Apollo Endosurgery
· Abbive
· FoodMarble
Conference Highlights
- Gastroenterology
- Gastrointestinal Infection and Viral Gastroenteritis
- Gastrointestinal Pharmacology
- Gall Bladder Cancer Treatment
- Advance Nutrition and Dietetics in Gastroenterology
- Gastrointestinal Oncology
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Kidney and Pancreas Transplant
- Liver & Intestine Transplant
- Gastrointestinal Diseases during Pregnancy
- Neuro gastroenterology Disorder
- Advanced Research in Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Disease of Liver Cancer
- Advanced Hepatology
- Hepatitis Infections
- Hepatitis Vaccination
- Hepato-pancreato-biliary disease
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Gastrointestinal and Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Metabolic liver diseases
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Obesity and Bariatric Surgery
- Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Pathology
- Hepatic Hemangioma
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 16-17, 2022 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Research and Reports in Gastroenterology
- Journal of Health and Medical Research
- Journal of Hepatology and Gastrointestinal disorders
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by





